Microsoft Windows servers to put a large-scale global cyber attack on Friday using ransomware, a malicious software that holds your computer hostage for ransom and a hacking tool stolen from the U.S. National Security Agency (NSA). The attack will leave victims locked and demands ransom and they will threat to destroy files if the ransom is not met. We rather not pay the ransom, mainly because it does not assure a solution to the problem. There could be bugs in the malware that makes the encrypted data which is not able to recover even with the right key.
In addition, if the ransom is paid, it proves to the cybercriminals that ransomware is effective. As a result, cybercriminals will continue their activity and look for new ways to exploit systems that result in more infections and more money on their accounts.
What is Ransomware?
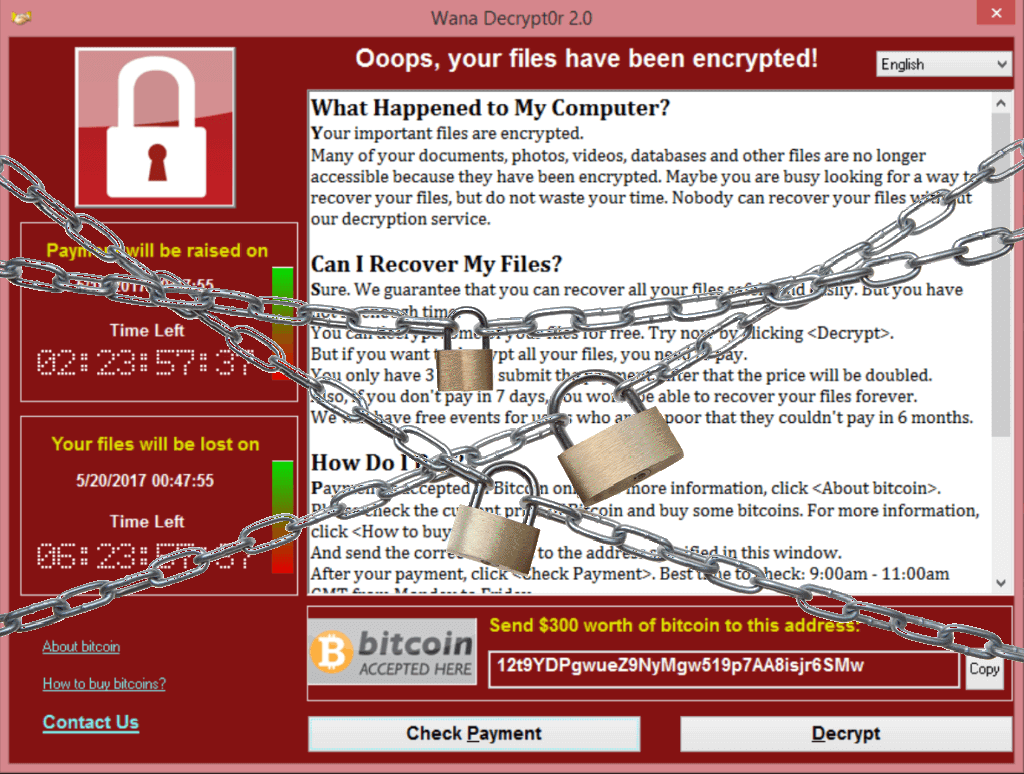
Ransomware is malicious code that is used by cybercriminals to blocks the victim’s access to his/her files. The intention for ransomware attacks is monetary, and unlike other types of attacks, the victim is usually notified that an exploit has occurred and is given instructions for how to recover from the attack. Payment is often demanded in virtual currency to protect the criminal’s identity. The malware, which spreads like a worm, is transmitted through email containing a compressed, encrypted file. gains access to a given device once the malware-filled file is downloaded: it then encrypts data, locks down the system and demands ransom In a lockscreen attack, the malware may change the victim’s login credentials for a computing device This may affect other connected network device. The malware spread rapidly by exploiting a security flaw in Microsoft Windows servers.
What users need to do
One should make sure whether your Microsoft Windows server is up to date. But those who did not apply the software update is left exposed to the hack. Install and use an up-to-date antivirus solution.
Avoid clicking on links or opening attachments or emails from people you don’t know or companies you don’t do business with.End users should beware of clicking on links in emails from strangers or opening email attachments and victims should do all they can to avoid paying ransoms.
Have a pop-up blocker running in your web browser.
Regularly backup your important files.
Microsoft recommends users upgrade to Windows 10 and install the security update MS17-010. With the 1.243.297.0 update, Windows Defender Antivirus detects the malware as Ransom:Win32/WannaCrypt.
The company also recommends Device Guard for businesses and Office 365 Advanced Threat Protection for blocking emails carrying malware.
How Ransomware approach a user :
The victim may receive a pop-up message or email warning that if the ransom is not paid by a certain date, the private key required to unlock the device or decrypt files will be destroyed.
The victim may be duped into believing he is the subject of an official inquiry. After being informed that unlicensed software or illegal web content has been found on his computer, the victim is given instructions for how to pay an electronic fine.
The attacker encrypts files on infected computed devices and makes money by selling a product that promises to help the victim unlock files and prevent future malware attacks.
Wasn’t the ransomware stopped?
The masterminds behind the attack can easily modify the code to get the ball rolling again. Since Friday, two new variations of the malware have been detected. As such, it maintains imperative for people to protect their computers.
While ransomware attacks may be nearly impossible to stop, there are important data protection measures individuals and organizations can take to insure that damage is minimal and recovery is a quick as possible. Strategies include compartmentalizing authentication systems and domains, keeping up-to-date storage snapshots outside the main storage pool and enforcing hard limits on who can access data and when access is permitted.